Understanding and responding to anabolic steroid injecting and hepatitis C risk in Australia
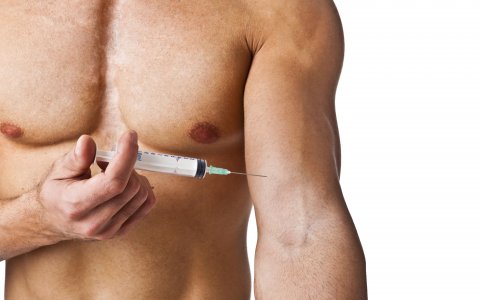
In recent years, several studies have suggested that the use of performance and image enhancing drugs via injection is increasing in Australia, with anabolic steroids appearing to be the most commonly used of these drugs. Traditionally the domain of elite athletes and recreational bodybuilders, steroid use may be extending to other groups, including adolescents, gym attendees, professionals and students. Like other forms of injecting drug use, steroid injecting can allow transmission of blood-borne viruses, especially hepatitis C, but little is known about how steroid injecting takes place and how such transmission might occur. Crucially, Australia’s existing harm reduction framework appears ill-equipped to deal with this emerging trend, and is underprepared to meet the challenges that it may pose. This commentary outlines key areas where more research into steroid use in Australia is needed. Improved understandings of the practices and experiences of individuals, who inject steroids, and the possibilities for targeted harm reduction responses, are needed if Australia is to respond to the increase in steroid use effectively.